Fluconazole
By N. Riordian. Colorado College.
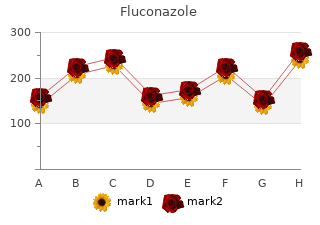
Usually buy fluconazole 200 mg fast delivery, as pregnancy progresses purchase 200 mg fluconazole free shipping, women instinctively alter exercise activity patterns. Women also need be aware to change or enhance exercise equipment, such as switching from supine to upright cycling. Historically, concern has been that intense physical activity could result in low birth weight infants and preterm delivery, but this concern needs to be balanced against the need to control body weight during pregnancy and afterward and current evidence that prudent physical activity per- formed at moderate intensities within current guidelines has no adverse effects on fetal development (Mottola and Wolfe, 2000). Exercise prescrip- tions for pregnant women are not dissimilar to those for other adults. Exercise sessions should be preceded by a 5- to 15-minute warm-up, and followed by a similar cool-down period. Exercise frequency should be 3 to 5 times per week, and not increase in frequency during first or third trimesters because of fatigue and an evaluation of risks to benefits. Exercise intensity should be moderate and elicit 60 to 70 percent Vo2max, which can be monitored by the maternal heart rate response as shown in Table 12-8. And finally, intensity can be gauged by the talk test, or exercise intensity where lactic acidosis drives pulmonary minute ventilation so that the pregnant woman is out of breath and cannot carry on a conversation. As stated in Chapter 4, the Dietary Reference Intakes are provided for the apparently healthy population, therefore recommended levels of physical activity that would result in weight loss of overweight or obese individuals are not provided. In terms of making a realistic physical activity recommendation for busy individuals to maintain their weight, it is important to recognize that exercise and activity recommendations consider “accumulated” physical activity. It is difficult to determine a quantifiable recommendation for physical activity based on reduced risk of chronic disease. Meeting the 60 minute/day physical activity recommendation, however, offers additional benefits in reducing risk of chronic diseases, for example, by favorably altering blood lipid profiles, changing body composition by decreasing body fat and increasing muscle mass, or both (Eliakim et al. For instance, in a study of Harvard alumni, mortality rates for men walking on average less than 9 miles each week were 15 percent higher than in men walking more than 9 miles a week (Paffenbarger et al. Moreover, in the same study, men who took up vigorous sports activities lowered their risk of death by 23 percent compared to those who remained sedentary (Paffenbarger et al. Similar favorable effects were observed in the Aerobics Center Longitudinal Study as men in the lowest quintile of fitness who improved their fitness to a moderate level, reduced mortality risk by 44 percent, an extent comparable to that achieved by smoking cessation (Blair et al. Results from observational and experimental studies of humans and laboratory animals provide biologically plausible insights into the benefits of regular physical activity on the delayed progression of several chronic diseases. The interrelationships between physical activity and cancer, cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes mellitus, obesity, and skeletal health are detailed in Chapter 3. Table 12-9 shows seven prospective studies that associated varying ranges of leisure time energy expenditure (kcal/day or kcal/week) with the risk of chronic diseases and/or associated mortality. Assuming an average of 150 kcal expended per 30 minutes of moderate physical activity (Leon et al. The required amount of physical activity depended on the endpoint being evaluated. The minimum amount of physical activity that provided a health benefit ranged from 15 to 60 minutes/day. The amount of physical activity that provided the lowest risk of morbidity and/or mortality was 60 to greater than 90 minutes/day. This recommendation is also consistent with Canada’s “Physical Activity Guide to Healthy Living” (Health Canada, 1998), and the World Health Organization technical report on obesity (2000). Specifically, recommendation number 3 in Chapter 2 of the Sur- geon General’s report states: “Recommendations from experts agree that for better health, physical activity should be performed regularly. The most recent recommendations advise people of all ages to include a minimum of 30 minutes of physical activity of moderate intensity (such as brisk walking) on most, if not all, days of the week. It is also acknowledged that for most people, greater health benefits can be obtained by engaging in physical activity of more vigorous intensity or of longer duration. Moreover, they showed that more vigorous exercise was associated with an increased degree of protection. Conversely, physical inactivity, noted by prolonged sitting, was shown to be a signifi- cant risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Similarly, reporting on treadmill evaluations of over 6,000 men studied over a 6-year period, Myers and coworkers (2002) concluded that “exer- cise capacity is a more powerful predictor of mortality among men than other established risk factors for cardiovascular disease. The vast majority of review articles have concluded that acute or chronic aerobic exercise is related to favorable changes in anxiety, depression, stress reactivity, positive mood, self-esteem, and cogni- tive functioning (Anthony, 1991; Craft and Landers, 1998; Landers and Arent, 2001; Mutrie, 2000; North et al. Although one reviewer (Mutrie, 2000) has argued for a causal relationship between exercise and the reduction of clinical depression, others suggest that there are not enough clinical trial studies to support a causal interpretation (Landers and Arent, 2001). Examination of the meta- analyses indicates that the overall magnitude of the effect of exercise on anxiety, depression, stress reactivity, and cognitive functioning ranges from small to moderate, but in all cases, these effects are statistically significant (Landers and Arent, 2001). These results are encouraging, but there is still much to learn before the relationship between physical activity and mental health can be fully understood.
Oral testimony presented by members of the public during the open sessions was also taken into account order fluconazole 200mg free shipping. Additional information was obtained from written testimony submitted to the committee (available from the National Academies’ Public Access Records Offce cheap fluconazole 50mg with mastercard, publicac@nas. However, treatment information can be found in guide- lines published by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (Ghany et al. The committee also has not been tasked with comprehensively review- ing information about the safety of the hepatitis B vaccine. The committee that wrote that report concluded that the evidence favored rejection of a causal relationship between hepatitis B vaccine administered to adults and incident multiple sclerosis and multiple- sclerosis relapse. It also found the evidence inadequate for accepting or rejecting a causal relationship between hepatitis B vaccine and the frst episode of a central nervous system demyelinating disorder, acute dissemi- nated encephalomyelitis, optic neuritis, transverse myelitis, Guillain-Barré syndrome, or brachial neuritis. Hepatitis and Liver Cancer: A National Strategy for Prevention and Control of Hepatitis B and C http://www. The committee that wrote the present report met fve times in the period December 2008–August 2009. During the meetings, the committee evalu- ated the evidence and deliberated on issues relevant to its charge. It also explored federal and state surveillance mechanisms for identifying and tracking hepatitis B and hepatitis C cases. The committee began by identifying problems with and gaps in the current prevention and control systems. The committee focused on making recommendations that could be implemented with existing knowledge and available tools to advance pre- vention and control of chronic viral hepatitis in a timely manner. Although the committee recognizes the importance of basic research in this feld, it believes that given the scope of the problem and the lack of available resources, its focus should be on improving prevention and control ser- vices. As a result, the committee did not address basic-research questions in the feld extensively. After defning the scope of the problem and reviewing the available evidence, the committee identifed the primary underlying factors that impede cur- rent efforts to prevent and control hepatitis B and hepatitis C. The com- mittee believes that a lack of awareness about viral hepatitis among both the general public and health-care and social-service providers is leading to continued high rates of morbidity and mortality from hepatitis B and hepatitis C. Consistent themes were found in all the materials reviewed by the committee; as a result, this report is organized according to four principal categories: • Improved disease surveillance (Chapter 2). Hepatitis and Liver Cancer: A National Strategy for Prevention and Control of Hepatitis B and C http://www. Hepatitis and Liver Cancer: A National Strategy for Prevention and Control of Hepatitis B and C http://www. Hepatocellular carcinoma inci-Hepatocellular carcinoma inci- dence, mortality, and survival trends in the United States from 1975 to 2005. Prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection among injection drug users in the United States, 1994-2004. The prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection in the United States, 1999 through 2002. Proceedings of the 0 international symposium on viral hepatitis and liver disease, edited by F. Screening for chronic hepatitis B among Asian/Pacifc Islander populations— New York City, 2005. Newborn hepatitis B vaccination coverage among children born January 2003- June 2005—United States. Hepatitis and Liver Cancer: A National Strategy for Prevention and Control of Hepatitis B and C http://www. Notice to readers: National hepatitis B initiative for Asian Americans/ Native Hawaiian and other Pacifc Islanders. The burden of liver cancer in Asians and Pacifc Islanders in the greater San Francisco Bay area, 1990 through 2004. The estimated direct medical cost of sexually transmitted diseases among American youth, 2000. Expected increase in hepatitis C-related mortality in Egypt due to pre-2000 infections. Elevated prevalence of hepatitis C infection in users of United States Veterans Medical Centers. TheThe injection century: Massive unsterileinjection century: Massive unsterile injections and the emergence of human pathogens. The role of parenteral antischistosomal therapy in the spread of hepatitis C virus in Egypt. Prevalence and incidence of hepatitis C virus infection among young adult injection drug users.
When these conditions obtain discount 50mg fluconazole amex, the womb ‘‘hits the liver and they go together and strike against the abdomen—for the womb rushes and goes upward towards the moisture fluconazole 200mg with visa. When the womb hits the liver, it produces sudden suffocation as it occupies the breathing passage around the belly. For example, when the womb strikes the liver or abdomen, ‘‘the woman turns up the whites of her eyes and becomes chilled; some women are livid. If the womb lingers near the liver and the abdomen, the woman dies of the suffocation. Multiple means of treat- ment were employed, including the recommendation that, when the womb moves to the hypochondria (the upper abdomen or perhaps the diaphragm), young widows or virgins be urged to marry (and preferably become preg- nant). This was premised, apparently,on the belief that thewombwas capable of sensing odors. Fetid odors (such as pitch, burnt hair, or castoreum) were applied to the nos- trils to repel the womb from the higher places to which it had strayed, while sweet-smelling substances were applied to the genitalia to coax the uterus back into its proper position. Not all the symptoms were listed every time uterine movement was men- tioned by the Hippocratic writers, nor did all cases of pnix involve uterine movement. Whenanattack occurs, sufferers from the disease collapse, show aphonia, labored breathing, a seizure of the senses, clenching of the teeth, stridor, convulsive contraction of the extremities (but sometimes only weakness), upper abdominal distention, retraction of the uterus, swelling of the thorax, bulging of the network of ves- sels of the face. The whole body is cool, covered with perspiration, the pulse stops or is very small. Critical to his views, and to all contemporary criticisms of the ‘‘wandering womb’’ (in- cluding Galen’s, as we shall see in a moment) were the anatomical discover- ies made at Alexandria in the third century . The womb ‘‘does not issue forth like a wild animal from the lair’’ but is instead ‘‘drawn together because of the stricture caused by the inflammation’’ of these uterine ligaments. Soranus also adamantly rejected the Hippocratic odoriferous therapy, or at least the part of it that employed foul- smelling substances. Yet for all his modifi- cations, Soranus never questioned the disease category itself. On the contrary, his thorough engagement with it was to help render it canonical in almost all later gynecological texts up through the Renaissance. Galen, active only a generation after Soranus, was more accommodating of traditional Hippocratic perspectives. Himself a highly experienced anato- mist,103 Galen no more than Soranus could accept the possibility that the womb actually wandered to various parts of the body since the diaphragm, if nothing else, absolutely prohibited movement to the thorax. He did not, however, question the by now traditional litany of symptoms, let alone the existence of the disease category. He, like Soranus, thought the womb could appear to be drawn up slightly because of inflammation of the ligaments. Yet to explain apnoia hysterike (difficulty of breathing caused by the uterus), Galen offered something of a compromise that would explain how the uterus, with- out moving to the upper parts, could still affect them. He posited a sympa- thetic poisonous reaction caused by either the menses or the woman’s own semen being retained in her uterus. Notable here is Galen’s shift in ideas about how semen and sexuality played into this dis- ease: for Galen, it was not her lack of semen provided by a man that made the widow susceptible, but the buildup of her own seed. Despite these dis- agreements,Galen maintained elements of the traditional odoriferous therapy, though he complemented this with bloodletting, massage, and a host of other treatments. Both Soranus and Galen represented the very highest theoretical tradi- tions of Greek medicine, catering as they did to the elite, Hellenized urban classes of Rome. Their views never eradicated what were apparently deeply rooted popular beliefs that the womb did indeed wander. Even Muscio, in the fifth or sixth century when hewas rendering Soranus into Latin, slipped in the more than suggestive phrase ‘‘when the womb moves upwards toward the chest’’ when referring to uterine suffocation; as he repeated this several times, it seems that he, too, thought the womb capable of more than ‘‘distension caused by the ligaments. One is written into a blank space of a late-ninth-century medical volume by a tenth-century Introduction hand. Having invoked the aid of the Holy Trinity, the nine orders of the an- gels, the patriarchs, prophets, apostles, martyrs, confessors, virgins, and ‘‘all the saints of God,’’ the priest is to command the womb to cease tormenting the afflicted woman: I conjure you, womb, by our lord Jesus Christ, who walked on the water with dry feet, who cured the infirm, shunned the demons, resuscitated the dead, by whose blood we are redeemed, by whose wounds we are cured, by whose bruise[s] we are healed, by him I conjure you not to harm this maidservant of God, [her name is then to be filled in], nor to hold on to her head, neck, throat, chest, ears, teeth, eyes, nostrils, shoulders, arms, hands, heart, stomach, liver, spleen, kidneys, back, sides, joints, navel, viscera, bladder, thighs, shins, ankles, feet,or toes, but to quietly remain in the placewhich God delegated to you, so that this handmaiden of God, [her name], might be cured. The chief vehicle for Galen’s views in the twelfth century was, of course, Ibn al-Jazzār’s Viaticum. In discussing uterine suffo- cation in book , Ibn al-Jazzār had echoed Galen in asserting that ‘‘the sperm increases, corrupts, and becomes like a poison. Ibn al-Jazzār postulated that the putrefying menses and/or semen in the uterus produced ‘‘a cold vapor’’ that rose to the diaphragm. In the main chapter on uterine suffocation (¶¶– ), the author closely follows the Viaticum in laying out the standard litany of symptoms, recounting Galen’s cure (from On the Affected Parts), and positing the same causation: corrupted semen (or menses) is turned into a ‘‘venom- ous nature,’’ and it is this ‘‘cold fumosity’’ that ascends up to ‘‘the parts which are commonly called the corneliei, which because they are close to the lungs and the heart and the other organs of the voice, produce an impediment of speaking. This chapter (¶) is drawn from the alternate source, the Hippocratic Book on Womanly Matters. In the ‘‘rough draft’’ of Con- ditions of Women,theTreatise on the Diseases of Women, it was stated very clearly that movement of the womb to the upper body was possible: ‘‘Sometimes the womb [moves] from its place, so that it ascends up to the horns of the lungs, that is, the pennas [feathers], and [sometimes] it descends so that it goes out Introduction of [the body] and then it produces pain in the left side. And it ascends to the stomach and swells up so much that nothing can be swallowed. The sign of this is that she feels pain in the left side, and she has distention of the limbs, difficulty swallowing, cramping, and rumbling of the belly.
The tracking of imaging procedures and radiation doses is recommended as a way for institutions and agencies to monitor trends in procedures and radiation doses delivered collectively to patients buy 200mg fluconazole amex. This process lends a sense of personal empowerment to individuals purchase fluconazole 150mg free shipping, but may also mislead patients into thinking that their collective exposure can be estimated by adding doses to different body regions from separate modalities. In any event, the decision to administer an imaging procedure to a patient should always be based on the benefits/risks of the procedure without regard to previous exposures the patient may have received. There was considerable discussion about justification and optimization of imaging procedures at the conference, while less attention was paid to proper implementation and evaluation of the procedures. The four elements collectively comprise the continuous quality improvement cycle for imaging procedures shown in Fig. It was recognized that both overutilization and underutilization of medical imaging compromise the concept of justification of imaging procedures. However, these shortcomings can be addressed relatively successfully through the use of decision support systems to guide the referring physician in selecting the proper imaging examination for the patient. Digital radiography presents a number of challenges with regard to patient protection and procedure optimization. Interventional procedures have increased remarkably over the past couple of decades, and have improved patient outcomes and reduced patient mortality and morbidity as a consequence. The Image Wisely campaign has been launched to improve quality and reduce dose in adult imaging in the manner so successfully achieved by the Image Gently campaign for paediatric imaging. Collaboration in this effort with organizations concerned with similar issues in other countries was encouraged. Anatomically correct phantoms for validation of Monte Carlo methods for organ dose calculations are being developed. Also of concern is the use of adjectives such as ‘low’, ‘very low’ and ‘ultra low’ as adjectives preceding dose in articles published in the literature. These terms are relative and vary with time, geographic location and patient size. The journal Radiology has stated that it will not accept these modifiers of dose in submitted papers, and the journal Medical Physics will take a similar position in the near future. Radiation oncology has changed radically over the past 2–3 decades, and today is a highly complex field dominated by software as well as sophisticated hardware. Non-standard photon and particle beams are widely used under conditions that can cause major errors if commissioning and ongoing quality control are inadequate. Several examples of such inadequacies were described in which patients were severely injured or killed by improper physics procedures. Other challenges of the modern era of radiation oncology include improved methods for in vivo dosimetry, better compensation for patient motion, increased biological understanding of individual differences in radiation sensitivity, and the propensity for developing second cancers, especially in children. New unsealed sources that target tumours through the use of antibodies, nanoparticles and tumour specific agents constitute an exciting arena for future developments. One observation made at the conference was that as the complexity of diagnostic and therapeutic devices increases, quality assurance measures must be simplified 1 www. The challenge of improving the care of patients in countries with greatly limited resources was raised several times during the conference, and was recognized as a great and unfulfilled need across the globe. It was widely recognized that health care is a collaborative partnership between those who provide care and those who receive it, and that true collaboration requires: (i) truthfulness and directness; (ii) partnership and collaboration; (iii) openness and transparency; (iv) understanding of benefits, risks and options; and (v) engagement and involvement of all parties. It was recognized that all medical procedures employing ionizing radiation should be provided within a culture of safety. Such a culture requires active leadership from the top, but is everyone’s responsibility if it is to be fulfilled. This process commenced for the 1996 edition with a review in 2006, followed by the decision to revise, commencing in 2007. It is crucial that only persons who meet particular requirements are allowed to act in these roles. Appropriately trained personnel will continue to underpin radiation protection in medicine in the next decade. It could be argued that, in the past, the level of implementation of the radiation protection principle of justification in medical exposure was not as good as it should have been, partly due to lack of clarity about who is responsible. Imaging is the area of medical uses of radiation where this is particularly a problem. On the one hand, the referring medical practitioner knows the patient, the medical history and the clinical context, while, on the other, the radiological medical practitioner has specialist knowledge about the proposed procedure — its benefits, risks and limitations. However, the practice of defensive medicine may lead to the referring medical practitioner requesting more procedures than necessary. In some countries, there may be a financial conflict of interest for the radiological medical practitioner — the more procedures performed, the greater the income. Fortunately there is a growing body of knowledge about the appropriateness of given examinations or procedures for given conditions — the so-called referral guidelines [3] or criteria of appropriateness [4] — and these act as a bridge between the referring and the radiological medical practitioner. The next decade will see the increasing role of software for referrals, with the incorporation of appropriateness criteria into such systems.