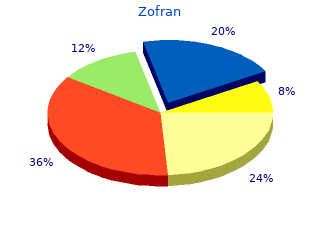
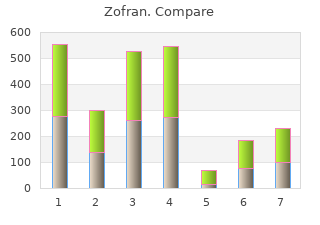
Zofran
2019, Florida Southern College, Enzo's review: "Zofran generic (Ondansetron) 8 mg, 4 mg. Purchase online Zofran no RX.".
It is also an excellent opportunity for the dentist to establish a relationship with the child and his or her parent generic zofran 4mg online. Generally speaking purchase zofran 4mg mastercard, information is best gathered by way of a relaxed conversation with the child and his or her parent in which the dentist assumes the role of an interested listener rather than that of an inquisitor. While some clinicians may prefer to employ a proforma to ensure the completeness of the process, this is less important than the adherence to a set routine. A complete case history should consist of: • personal details; • presenting complaint(s); • social history; • medical history; • dental history. Where these details have been entered in the case notes prior to the appointment they should be verified. However, since some parents will consider this kind of information confidential, the dentist may need to exercise considerable tact in order to obtain it. This stage of history-taking also presents an opportunity to engage the child in conversation. Conditions that will be of significance include allergies, severe asthma, diabetes, cerebral palsy, cardiac conditions, haematological disorders, and oncology. Wherever possible, a comprehensive medical history should commence with information relating to pregnancy and birth, the neonatal period, and early childhood. Previous and current problems associated with each of the major systems should be elicited through careful questioning, and here a proforma may well be helpful. Details about previous hospitalizations, operations (or planned operations), illnesses, allergies (particularly adverse reactions to drugs), and traumatic injuries should be recorded, as well as those relating to previous and current medical treatment. It is useful to end by asking the parent whether there is anything else that they think the dentist should know about their child. Key Point Sensitive questioning is required if the child appears to have a behavioural problem that has not been mentioned by the parent during the formal medical history. It is important to bear in mind that many children with significant medical problems will have been subjected to multiple hospital admissions/attendances. These experiences may have a negative effect on the attitude of both the child and his or her parents towards dental treatment; in addition, dental care may not be seen as a priority in the context of total care. Finally, a brief enquiry should also be made regarding the health of siblings and close family. Significant family medical problems, for instance problems in relation to general anaesthesia, may not only alert the practitioner to potential risks for the child, but may also be factors to consider when treatment planning. Likewise, if the patient has a sick sibling, it may not be possible for the parents to commit to a prolonged course of dental treatment. In so doing, specific procedures may emerge as having proved particularly problematic; such prior knowledge will enable the dentist to modify the treatment plan appropriately. The dental history should also identify factors that have been responsible for existing oral and dental problems as well as those which might have an impact on future health. These include dietary, oral hygiene, dummy/digit sucking, and parafunctional habits. Specific questions should be asked about drinks (particularly the use of a bottle at bedtime in the younger age group,), between-meal snacks, frequency of brushing, and type of toothpaste used. Key Point Embarking on a treatment plan that is at significant variance with parental attitudes and expectations without clear explanation and justification invites non-completion. In an ideal world, unco-operative children would be given the time and opportunity to voluntarily accept a dental examination over a series of desensitizing visits. In reality, if a child presents with a reported problem but remains unco-operative after gentle coaxing and normal behaviour management strategies, restraint may be necessary. Physical restraint should only be considered for infants/very young children, or children with severe learning difficulties (providing they are not too big or strong to make any restraint potentially dangerous or uncontrolled). The issue of informed consent is important here, as it is imperative that the need for the examination and the manner in which it is going to be conducted is clearly understood by all concerned. It is best to: • explain in advance how the child is to be positioned, • ask parents for their active help, • give reassurance that the child is not going to be hurt in any way. In a few cases, it may be appropriate to take an accurate height measurement (Fig. Children whose height lies below the third centile, above the ninety-seventh centile, or who exhibit less than 3-5 cm growth per year should be referred to a paediatrician for further investigation; • weight⎯could there be an underlying eating disorder? The head and neck During the examination of the head and neck, the following structures should be briefly assessed: • head⎯note size, shape (abnormalities may be seen in certain syndromes), and any facial asymmetry (Fig. Obviously, when the child presents with a specific problem, such as a facial swelling, a more thorough examination of the presenting condition is needed (see Chapter 15). The following is a suggested order: • soft tissues • gingival and periodontal tissues • teeth • occlusion. Soft tissues An abnormal appearance of the oral soft tissues may be indicative of an underlying systemic disease or nutritional deficiency. In addition, a variety of oral pathologies may be seen in children (see Chapter 15). It is therefore important to carefully examine the tongue, palate, throat, and cheeks, noting any colour changes, ulceration, swelling, or other pathology (Fig. It is also sensible to check for abnormal frenal attachment or tongue-tie, which may have functional implications.
Auditory neuropa- tory neuropathy is the results of mutations in the otoferlin thy in patients carrying mutations in the otoferlin gene order 4 mg zofran with mastercard. Auditory neuropathy: an historical and current perspec- ment: principles and guidelines for early hearing detection and tive purchase 4 mg zofran with amex. The characteristics of these changes tion, as a result of age-related changes, this number continuously appear to be similar to those of salicylate-induced tinnitus in diminishes during the course of one’s life. This suggests that, at least in part, salicylate- of these hair cells, one can understand the need to protect the induced tinnitus is associated with dysfunction of the cochlear cochlea against the dangers of modern life, including certain med- nerve. In the United States, hearing loss linked to taking drugs at the periphery is responsible for the occurrence of tinnitus affects 2 to 3 patients per 1000. Cisplatin, a chemother- apeutic agent used in certain types of cancer, destroys the sensory hair cells, leading to irreversible hearing loss. Among factors Molecular mechanisms responsible having a harmful effect on hearing, noise is the most dangerous. Hearing loss is one of the commonest complaints in the work- for deafness place, and industrial noise has a considerable effect on hearing. More so than hearing loss, tinnitus strongly interferes with Exposure to noise or ototoxic drugs (aminoglycosides antibi- the daily lives of millions of people. Apoptosis is an active process of programmed cell subjective perception of sound in the absence of an external death (8) characterised by chromatin condensation, intracellular stimulus, animal models are difficult to establish. A schematic drawing of the cell death of salicylate, the active component of aspirin known to induce pathway that participates in apoptosis is given in Figure 20. Whatever the mechanism triggering lated cytoplasm, but intact lateral membrane) and of apoptosis neuronal death (lack of presynaptic target or excitotoxicity), (shrinkage of the cell body, increased electron density of the recent studies have suggested that an apoptotic process is cytoplasm, chromatin compaction with an intact lateral mem- involved, as in the hair cells (11). These diverse responses converge on mitochondria, often through the activation of proapoptotic members of the Bcl-2 family (e. These proapoptosis cytosolic forms of the Bcl-2 family represent pools of inactive, but potentially lethal proteins. Proapoptotic signals activate and redirect these proteins to the mitochondria, where they interact with antiapoptotic molecules such as Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL at the outer membrane of the mitochondria, where they compete to regulate the formation of pores and the release of cytochrome C from the mitochondria into the cytosol of the affected cell. The cytochrome C associates with Apaf-1, procaspase-9 to form an apoptosome complex. The apoptosome activates procaspase-9, which in turn activates downstream effector caspases (e. The cell death-receptor and mitochondrial cell death pathways converge at the level of procaspase-3 activation. Caspase-8–mediated cleavage of Bid, a proapoptotic Bcl-2 family member, greatly increases its proapoptotic activity and results in its translocation from the cytosol to the outer mitochondria membrane, where it promotes the formation of pores by Bax and the release of cytochrome C. Innovative therapeutical strategies to prevent deafness and to treat tinnitus 273 degeneration of the noise-damaged hair cells involves different mechanisms of cell death, including typical apoptosis, autolysis, and, to a lesser extent, necrosis. Indeed, intracochlear perfusion of glutamate antagonists prevents 50% of the acute threshold eleva- tion by protecting the neuronal endings of the cochlear nerve, but it has no protective effect on the hair cells themselves (13). Pharmacological strategies have also been used to protect the cochlea against noise trauma. Corticosteroid therapy has been reported to have a significant effect when applied intraperi- toneally (i. Recent years have seen increasing interest in the development of local delivery of pharmacological agents to protect the cochlea from noise trauma. Free radical scavengers such as mannitol or deferoxamine are much less potent than glutamate antagonists at preventing acute threshold elevation, but they can reduce hair cell loss by 40% (15). Neurotrophins have also been evaluated as a local protective pharmacological strategy. In these experiments, neurotrophin-3 and glial cell line–derived neurotrophic factor have been shown to rescue 11% of hair cells and to slightly Figure 20. The attenuate apoptotic and necrotic cell death in rat models of spinal mitochondria are altered (arrows), but the cytoplasmic lateral membrane is cord (16) and retinal (17) ischaemia. Note the swollen afferent dendrites (asterisks) at the basal pole of the Wang et al. This hair cell shows riluzole against noise-induced hearing loss in the cochlea of the shrinkage of the cell body and increased electron density of the cytoplasm. Intracochlear perfusion of riluzole protects guinea cytoplasmic lateral membrane is preserved. All afferent endings are totally pig cochleas from damage caused by acoustic trauma, as demon- disrupted (asterisks). Sign of necrosis: distorted mitochondria (small black arrows) and exposed controls one month after noise trauma (Fig. The average hearing thresholds measured 20 minutes after acoustic trauma were 60 to 70dB between 12 and 16kHz (Fig. Thus, the different patterns of caspase-8 tion of initiator and effector caspases. Further func- apoptosis is supported by the results of recent studies on noise tional data reported in our study reveal that local scala tympani trauma (10,19).
So it is indicated only when there is severe oedema resistant to large doses of diuretics and if the nephrotic patient is to be subjected to surgery or invasive procedure (e purchase zofran 4 mg overnight delivery. This improves circulating blood volume and prevents hypotension or shock during the procedure purchase 4mg zofran with mastercard. Corticosteroids are given when there is no response to previous lines of treatment. Minimal change glomerulonephritis gives the best response while mesangiocapillary glomerulonephritis is always steroid resistant. The dose and duration of steroid treatment depends on the type of disease and response. In primary (idiopathic) minimal change nephritis 40-60 mg daily prednisone are given orally (for children 1- 2 mg/kg/d), for 4-6 weeks followed by gradual withdrawal. Other immunosuppressive drugs as cyclophosphamide, azathioprine and ciclosporin are indicated in selected cases. The period between infection and the appearance of glomerulonephritis (latent period) is 1-3 weeks for pharyngeal infection and 2-4 weeks for skin infection. Clinical picture: Usually the patients present with manifestations of acute nephritic syndrome with oliguria, smoky urine, puffiness of the face and headache (as a result of hypertension). Some patients may develop encephalopathy as a result of severe hypertension or hyponatraemia or they develop heart failure because of hypertension and fluid retention. Streptococcal antigens stimulate the body to form antibodies against them with the subsequent immune complex formation. Urine may show red cell casts, proteinuria (less than in nephrotic syndrome), haematuria or leucocyturia. Severe cases may show glomerular crescents (cases presenting clinically with rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis). Treatment: Treatment of poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis is mainly symptomatic (rest, salt restriction, diuretics, antihypertensives, treatment of infection and dialysis if renal failure develops). Prognosis: Most of the cases (85%) recover completely, 5% die in early phases from complications (hypertensive encephalopathy or heart failure). The rest of the cases pass to chronic glomerulonephritis and develop chronic renal failure. Signs of bad prognosis are persistently rising serum creatinine, heavy proteinuria, persistent hypertension with gross haematuria and presence of glomerular crescents in renal biopsy. Renal involvement may be the dominant lesion or may be just an incidental finding. Generally, when the kidney is involved, the prognosis and type of treatment are changed drastically. It affects caucasian more than black and occurs more in adolescents than in elderly. Most probably the disease reflects an exaggerated response to common environmental agents in a genetically susceptible host. But, if kidney biopsies are obtained and examined thoroughly, all patients will show glomerular disease. In clinical practice lupus nephritis is responsible for more than 5% of patients presenting with glomerulonephritis. Clinical Manifestations of Lupus Nephritis: It is known that 50-90% of lupus patients will show manifestation(s) of renal disease. Many of such patients may not show any clinically apparent renal disease, but when subjected to kidney biopsy glomerular lesions will be detected. Clinical presentation of lupus nephritis patient may vary from asymptomatic urine abnormality to rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis. Furthermore, some patients show manifestations of tubulointerstitial nephritis (e. Treatment: There is no standard regimen for the treatment of lupus nephritis patient. The available treatment protocols include: (1) Prednisolone, oral, 1mg/kg/d, (2) 3-5 days pulses of methyl prednisolone 500-1000 mg each, (3) Cytoxan (cyclophosphamide) 2-3 mg/kg orally/d (4) cytoxan 0. Generally, the target of treatment is to induce remission, then to maintain it by small doses of either one drug (Prednisolone) or combined (e. The more active the disease, the more aggressive the treatment will be and vice versa. The classic type of polyarteritis nodosa may present with ischaemic renal changes, hypertension, immobilization with renal infarctions or haemorrhage related to the kidney (haematuria, peri-renal hematoma resulting from rupture of aneurysm). Treatment: Patients with active urine sediment (proteinuria, haematuria, casts), renal impairment and documented lesions in renal biopsy should be treated by immunosuppressive drugs to achieve remission. The dose and whether prednisolone alone or combined drug regimen, depend on disease activity and initial reponse to treatment. Cyclosporin A 5mg/kg/d can be used when these drugs are toxic or have no satisfactory response. Renal involvement is documented in 10-30% of the cases, but in some series, it reaches up to 90% of the cases.