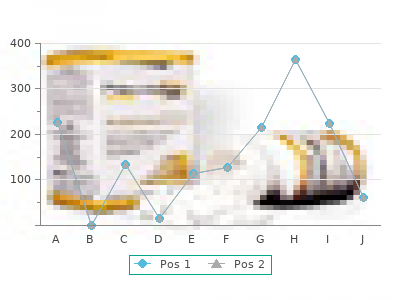
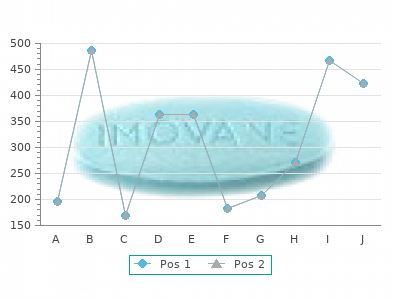
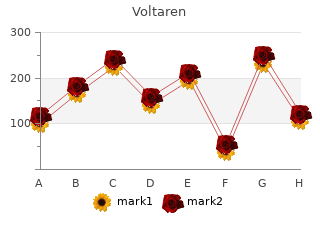
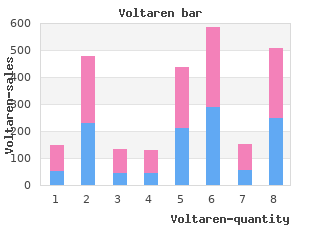
Voltaren
By O. Ayitos. University of Alaska, Anchorage.
Patients suspected of having connective tissue disease such as Marfan syndrome or Ehlers–Danlos syndrome should have echocardiography order voltaren 100mg free shipping. Specifically order voltaren 100 mg visa, echocar- diogram is used to evaluate the aortic root in individuals with suspected Marfan syndrome and to evaluate for Mitral Valve prolapse. Echocardiography is indicated for surveillance in various genetic disorders (Table 4. Patients diagnosed with Tuberous Sclerosis should undergo echocar- diography to evaluate for rhabdomyomas. Since this is an autosomal dominant disease with various organ involvements, echocardiography is useful in screening family members. Other appropriate indications for ordering an echocardiogram include workup of possible Rheumatic fever to look for evidence of carditis, infectious endocarditis to rule out vegetation, or valve lesions associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Saline contrast echocardiography should be requested in cases of stroke to rule out 62 W. Not associated with additional congenital heart disease Marfan syndrome Aortic root dilation, aortic dissection, mitral valve prolapse and regurgitation Neurofibromatosis Neurofibromata of the heart, renal artery stenosis, and renal hypertension (continued) 4 Pediatric Echocardiography 63 Table 4. Another rare indication for contrast echocardiography is in patients with Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia, in which pulmonary arteriovenous malformations can be life- threatening. In patients exposed to potentially cardiotoxic agents, such as chemotherapy including anthracyclines, baseline and routine interval follow-up echocardiograms are used to follow left ventricular function. When to Request a Cardiac Consultation First In infants outside of the neonatal period, children, and adolescents with a possible pathologic murmur or other abnormal cardiac auscultation finding, it is usually most effective and efficient to start with the cardiologist’s evaluation. In many cases the murmur or other finding may be determined to be innocent and echocardiogra- phy is not required. When echocardiography is indicated, the study is often assisted by having specific likely diagnoses listed based on the cardiologist’s assessment, and decisions about need for sedation, timing of study, and immediate interpreta- tion of results to patient and family is facilitated. Likewise, patients with other findings such as tachypnea, failure to thrive, or cyanosis are best referred to the cardiologist, rather that ordering an echocardiogram directly. The workup of stridor and/or difficulty in swallowing should exclude a possible vascular ring, which can be definitively diagnosed by echocardiography, but can be difficult, especially in laboratories with little experience in aortic arch anomalies in small children. Chest pain is common in older children and adolescents and, unless associated with exertion, is usually not due to cardiac disease. Echocardiography is rarely needed, as careful history and physical examination, are usually all that is required to exclude heart disease. Likewise, syncope, unless during exercise, is usually not due to structural heart disease and often does not need echocardiography in the workup. An abnormal electrocardiogram should first be confirmed by a cardiologist prior to decisions about further testing such as echocardiography. Screening for occult heart disease in patients being considered for use of stimu- lant medication or as part of pre sports participation evaluation requires careful and directed history and physical examination, but does not include screening echocar- diography. If further concerns arise, the patient should then be referred to a cardiologist for further evaluation. What to Expect from an Echocardiogram Echocardiography is the imaging modality of choice for defining intracardiac anatomy of congenital heart defects. The connections of major systemic veins and pulmonary veins can be defined, as well as the pulmonary arteries and the aortic arch with its major branches. In most cases, coronaries arteries, at least proximally, can also be imaged and their origins clearly defined. Doppler technology allows the detection of blood flow velocity and direction, and provides an ability to estimate pressures and pressure gradients. Color Doppler enables detection of shunting, even in cases where defects are too small to detect by imaging. In addition, global systolic and diastolic function as well as regional wall mechanics can now be investigated in detail. Stress echocardiogra- phy can assess changes in hemodynamics and function with exertion. Limitations of Echocardiography Echocardiography is highly dependent on the skill, expertise, and experience of the sonographer and the interpreting physician. Important congenital defects can be missed due to incomplete or inadequate imaging or to incorrect interpretation of the images. Ultrasonography requires adequate tissue windows, without interference from air or other structures that reflect sound. In certain conditions, such as severe obesity, pneumothorax or pneumomediastinum, severe scoliosis or pectus excavatum, or when chest bandages are present, adequate windows cannot be obtained. Chapter 5 Cardiac Catheterization in Children: Diagnosis and Therapy Anas Saleh Lutfi Taqatqa, Umang Gupta, Ra-id Abdulla, and Ziyad M. Hijazi Key Facts • Diagnostic cardiac catheterization is performed with much less frequency than the past due to advancement of other, less invasive, imaging modali- ties. Diagnostic cardiac catheterization may be required if other imaging modalities are not informative, hemodynamic evaluation to assess extent of shunts, cardiac output and pressure measurements are needed.
Dyskeratosis Congenita Definition Dyskeratosis congenita voltaren 100mg line, or Zinsser–Engman–Cole syn- drome buy voltaren 100 mg otc, is an uncommon disorder. Clinical features It is characterized by hyperpigmentation, atrophic skin areas, telangiectasia, nail dystrophy, hyperhidrosis, skin and mu- cosal bullae, blepharitis and ectropion, anemia, and oral manifestations. The oral lesions consist of recurrent blisters, epithelial atrophy, and leukoplakia (Fig. Differential diagnosis Leukoplakia, lichen planus, epidermolysis bul- losa, pachyonychia congenita. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license 32 White Lesions Pachyonychia Congenita Definition Pachyonychia congenita, or Jadassohn–Lewandowski syn- drome, is an uncommon genodermatosis. Clinical features It is characterized by symmetrical nail thickening, palmoplantar hyperkeratosis, hyperhidrosis, blister formation, follicular keratosis, and oral lesions. The oral lesions appear at birth or shortly afterward, and present as thick and white or grayish-white plaques, usually on the buccal mucosa, the tongue, and the gingiva (Fig. Differential diagnosis Dyskeratosis congenita, leukoplakia, lichen pla- nus, white sponge nevus, and focal palmoplantar and oral mucosa hyper- keratosis syndrome. Focal Palmoplantar and Oral Mucosa Hyperkeratosis Syndrome Definition This is a rare mucocutaneous disorder. Clinical features The main clinical manifestations are focal hyperker- atosis on the weight-bearing and pressure-related regions of the palms, soles, and oral mucosa (Fig. The oral lesions present as white hyper- keratotic plaques (leukoplakia), mainly on the attached gingiva, the lateral border of the tongue, and the palate (Fig. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license 34 White Lesions Differential diagnosis Pachyonychia congenita, dyskeratosis congeni- ta, leukoplakia. Characteristically, the tumor has a white or normal color, with numerous fingerlike projections that form a cauliflower pattern (Fig. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license 36 White Lesions Verrucous Carcinoma Definition Verrucous carcinoma is a low-grade variant of squamous- cell carcinoma. Clinical features Clinically, it presents as an exophytic white mass with a verrucous or pebbly surface (Fig. The buccal mucosa, palate, and alveolar mucosa are the most common sites of involvement. Differential diagnosis Verrucous leukoplakia, papilloma, verruciform xanthoma, white sponge nevus, squamous-cell carcinoma. Squamous-Cell Carcinoma Squamous-cell carcinoma has a wide spectrum of clinical features (see p. In about 5–8% of cases, it appears in the early stages as a white asymptomatic plaque identical to leukoplakia (Fig. Biopsy and his- topathological examination are important for the diagnosis in these cases. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license 38 White Lesions Skin and Mucosal Grafts Definition Skin and mucosal grafts are often utilized in the oral cavity to cover mucosal defects after extensive surgery for benign and malig- nant tumors, or as free gingival graft. Clinical features Clinically, both forms of grafts (skin and mucosal) usually present as a whitish, or gray-white plaque (Figs. Occasionally, the color of the skin graft is black, due to melanin overproduction. The tongue, buccal mucosa, palate, gingiva and alveolar mucosa are the most common sites where skin and mucosal grafts are placed. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license 40 White Lesions Epithelial Peeling Definition Epithelial peeling is a relatively common superficial des- quamation (epitheliolysis) of the oral mucosa. Etiology It is caused by the direct irritating effect of toothpastes that contain sodium lauryl sulfate or pyrophosphates. Clinical features Clinically, epithelial peeling presents as superficial painless white plaques or dots that can be easily lifted fromthe oral mucosa (Figs. The buccal mucosa, lip mucosa, and mucobuccal and mucolabial folds are more frequently affected. The lesions usually disappear when the individual stops using these toothpastes or mouth- washes. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license Laskaris, Pocket Atlas of Oral Diseases © 2006 Thieme All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license White Lesions 43 2 Red Lesions Red lesions are a large, heterogeneous group of disorders of the oral mucosa. Traumatic lesions, infections, developmental anomalies, allergic reactions, immunologically mediated diseases, premalignant lesions, malignant neoplasms, and systemic diseases are included in this group. The red color of the lesions may be due to thin epithelium, inflammation, dilatation of blood vessels or increased numbers of blood vessels, and extravasation of blood into the oral soft tissues. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license 44 Red Lesions Traumatic Erythema Definition and etiology Traumatic erythema occurs when a traumatic effect results in hemorrhage within the oral tissues.
The residual is measured at the faucet most distant from the where chlorine is added to the water supply buy voltaren 50mg lowest price. To ensure the proper contact time of at least 30 minutes order voltaren 50mg fast delivery, a holding tank can be installed (Table 5). Pressure tanks, while often thought to be sufficient, are usually too small to always provide 30 minutes of contact time. Available contact time from a 50-gallon holding tank Water flow rate (gallons per minute) Holding time (minutes) 5 7 7 5 10 3. Available contact time from 1000 feet of 1-1/4 inch pipe Water flow rate (gallons per minute) Holding time (minutes) 5 9. For superchlorination, a chlorine solution is added to the water to produce a chlorine residual of between 3. The necessary contact time for this concentration is reduced to less than five minutes (Table 4). If this is not desirable, the chlorine can be removed just before it is used with a carbon filter (Note: may not be currently allowed under your Department of Health for private water supplies). Oxidation Chemistry Oxidation chemistry has long been an accepted and effective part of many water treatment programs. Oxidizing microbiocides are often found at the forefront of many cooling water treatment programs. In large volume or once-through cooling systems they are usually the primary biocide and often are the most cost-effective programs available to a plant. When selecting these economical and versatile chemicals, several factors should be considered before a technically sound program is implemented. Environmental and regulatory impact, system pH, process contamination, and equipment capital and maintenance expense all play a role in the decision- making process. The primary killing mechanism these types of microbiocides use is oxidizing protein groups within a microorganism. Proteins are the basic components of essential cellular enzymes that are necessary for life-sustaining cellular processes such as respiration. The destruction of these proteins deprives the cell of its ability to carry out fundamental life functions and quickly kills it. One oxidant is chlorine dioxide, which appears to provide an additional killing mechanism. Chlorine dioxide is able to diffuse readily through hydrophobic lipid layers of an organism, allowing it to react with cellular amino acids, which directly inhibits protein synthesis. Since amino acids are the basic building blocks of all cellular proteins, destruction of these molecules has a devastating effect on the microorganism. Waterborne Diseases ©6/1/2018 475 (866) 557-1746 Staff shall be familiar with the locations of the chemical feed building as indicated by a posted site plan. Emergency repair kits “B” and “C” should be stored on site close to the chemical feed building. Chlorine scrubber Waterborne Diseases ©6/1/2018 476 (866) 557-1746 Chlorine Gas Section Chlorine Gas Background: Chlorine gas is a pulmonary irritant with intermediate water solubility that causes acute damage in the upper and lower respiratory tract. Of the 70,552 American soldiers poisoned with various gasses in World War I, 1843 were exposed to chlorine gas. Because its density is greater than that of air, the gas settles low to the ground. Cl2 gas does not occur naturally, although Chlorine can be found in a number of compounds. It has traditionally been the biocide of choice in many cooling water treatment systems. This dissociation phenomenon is important to remember when working with systems that will operate at a higher pH. Waterborne Diseases ©6/1/2018 477 (866) 557-1746 It is also widely known that chlorine is non-selective, making it very sensitive to contamination from either cooling water makeup or from in-plant process leaks. The combination of high chlorine demand in process-contaminated systems and the dissociation process in alkaline systems creates the need for greater chlorine feed to obtain the same microbial efficacy. In low pH water the passive metal oxide layers protecting the metal may resolubulize, exposing the surface to corrosion. The chloride ion (Cl ) can damage or penetrate the passive oxide layer, leading to- localized damage of the metal surface. High chlorine concentrations have also been shown to directly attack traditional organic-based corrosion inhibitors. When these inhibitors are "deactivated," the metal surface would then be susceptible to corrosion. Pathophysiology Chlorine is a greenish-yellow, noncombustible gas at room temperature and atmospheric pressure.